
Arq protocol full#
In Hybrid ARQ Type II, also known as full Incremental Redundancy (IR), each retransmission is not necessarily identical to the original transmission. Chase combining does not give any additional coding gain, it only increases the accumulated received signal to noise ratio for each retransmission. The receiver then uses maximum ratio combining to combine each received channel bit with any previous transmissions of the same bit and the combined signal is fed to the decoder. After each failed retransmission the erroneous packets are stored in a buffer. Hybrid ARQ Type I can be extended to include packet combining, this is known as Hybrid ARQ Type I with Packet Combing or Chase Combining. The transmitter will then retransmit the same packet until the packet is successfully decoded by the receiver or the maximum retransmission limit is reached. If a packet is found to be in error a retransmission request will be sent to the transmitter and the erroneous packet will be discarded. The simplest method: Hybrid ARQ Type I uses the CRC to detect whether or not an error in transmission has occurred. There are three types of Hybrid ARQ: Type I, Type-II and Type-III.

HARQ is able to compensate for link adaptation errors and provides a finer granularity of coding rate, resulting in better throughput performance than other FEC schemes. Hybrid-ARQ schemes are commonly used to facilitate reliable communication over noisy wireless channels.

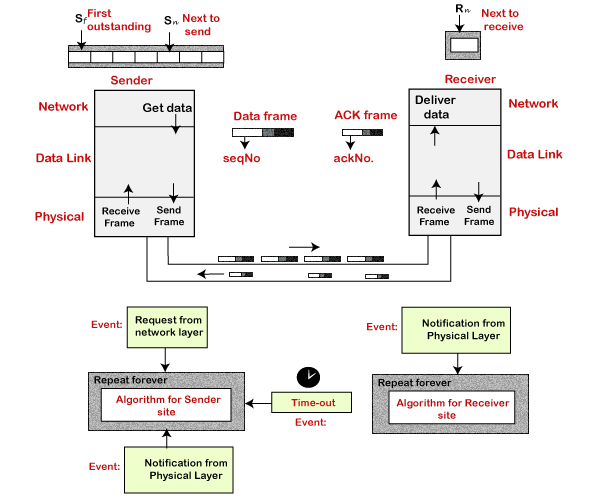
Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (Hybrid-ARQ) is a combination of Forward Error Correction (FEC) and Automatic Repeat reQuest in an optimal manner. The setup used in this example is based on Fixed Reference Channel R.3 defined in Table A.3.3.1-2 of TS36.101. The DL-SCH transmission is 16QAM modulated with a 1/2 target coding rate transmitted over single antenna port. This example demonstrates how a transmitter retransmits a single codeword over a single layer, using a different Redundancy Version (RV) each time until the CRC of the received codeword indicates a successful transmission. The Downlink Shared Channel (DL-SCH) is described in TS36.212, Section 5.3.2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
